@kalafina The fog client runs snapins as the system user. It looks like it also may be running the 32 bit version of powershell but he module is specifying 64 bit in the manifest or something like that. What does your snapin definition look like in the gui ?
Posts
-
RE: failed to import moduleposted in Windows Problems
-
RE: Printer mapping wont workposted in Windows Problems
@RTOadmin Can you provide
some examples of what you see working on the fog side and what you see not ?
The log of what’s broken ?
Version of fog and fog client ? -
RE: HP EliteBook 840 G9 - Cannot deploy imageposted in Hardware Compatibility
@DC09 I would suggest trying the dev-branch.
where you have the git fog fog cloned rungit checkout dev-branchthen do agit pulland then run that installer to update to the latest “dev” version.I would also try, with or without that, updating your bzImage kernel, there’s a thing in the gui for that see also https://docs.fogproject.org/en/latest/management/other-settings.html?highlight=Kernel#updating-the-kernel
I am using the dev version and kernel version 5.15.68 and recently imaged some hp eliteOne 840 G9’s without issue. All in ones, Not laptops, but similar enough models I’m sure
-
RE: Copy Cloud Storage of /images to Remote Servers Globallyposted in General
@typotony That’s Great to hear!
Glad you got it working and that it was as easy as intended. -
RE: Powershell API Moduleposted in Tutorials
@JJ-Fullmer
A new version has been published!Release notes here:
https://github.com/darksidemilk/FogApi/releases/tag/2303.5.26
-
RE: Copy Cloud Storage of /images to Remote Servers Globallyposted in General
@typotony You’re missing a
-where you’re defining the-fogserveryou’re also adding a-into it, it’s-fogservernotfog-serverfog-serveris the default value for that setting. You can also try just runningset-fogserversettings -interactivewithout params and it should prompt you for each value. You also don’t want http in there, just the hostname (ip should work fine too but I haven’t tested that, but its just pulled in as a string into the url, so no reason it wouldn’t work)Set-FogServerSettings -fogApiToken 'mytoken' -fogUserToken 'mytoken' -fog-server '192.168.150.25';That should do the trick
-
RE: Copy Cloud Storage of /images to Remote Servers Globallyposted in General
@typotony I had a chance to test things on linux with the examples I gave and all works swimmingly.
You can install pwsh on linux a few different ways, I usually user snap because it works the same on all distros. I used the LTS version. Microsoft’s instructions are found here https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/powershell/scripting/install/install-other-linux?view=powershell-7.3
Here’s the commands in redhat based linux I use to get pwsh installed. I imagine you could simply swap yum fo apt/apt-get in debian distros for that first command
prefix sudo if you’re not running as root.yum -y install snapd #create this symlink to be able to use "classic" snaps required by the pwsh package ln -s /var/lib/snapd/snap /snap #enable and start snapd services systemctl enable --now snapd.socket systemctl enable --now snapd.service systemctl start snapd.service systemctl start snapd.socket #install LTS pwsh snap install powershell --channel=lts/stable --classic #start pwsh (you may have to logout/login to refresh your path) pwshBottom line though, you can automate the export and import operations using the api. My examples here use json but you could also use
Export-csvto save the definitions as csvs but you’d then have to import them as objects and convert them to jsons, all of which there are built in functions for, but json is a bit simpler for this I think.In order to do a multi-direction sync, you’ll probably need to add some extra processing to the export. i.e. check the
.deployedvariable in each image definition to determine if it has been updated and only export it then if that already exists.To automate this, once you’ve configured the fogApi on each fog server those settings are saved securely for that user, so you can make a script for this that you plop in a cronjob for exporting and importing. i.e you do an export from each server to the
/images/imageDefinitionsfolder
before your sync of the /images directory to cloud, then after you pull the latest you run the import that will add new ones and update existing ones.For reference
To test this:
On my prod server I installed pwsh and the fogApi module and I made a new folder at /images/imageDefinitions and used the export-imagedefinitions function I put in my last comment to export the json definitions of each image to there.In my dev server I mounted a clone of the /images disk from my prod server to /images (could have also mounted the nfs share and rsynced them, this was just faster for me at the time) Then installed pwsh and the module. Then I ran the import-imageDefinitions function specifiying the import path of /images/imageDefinitions. It added all the definitions and all the images show up and are ready to be used on the dev server.
I will probably add a general version of the export and import functions to the api as this could be handy for migrating servers in general.
-
RE: ipxe boot slow after changing to HTTPSposted in FOG Problems
@brakcounty and @Sebastian-Roth
I recently did a fresh install of a fog dev server and did https and experienced similar slowness on the kernel loading.
I’ll give some of this testing a try and report back to see if this is maybe more common than we think. -
RE: Copy Cloud Storage of /images to Remote Servers Globallyposted in General
@george1421 said in Copy Cloud Storage of /images to Remote Servers Globally:
@JJ-Fullmer do you know if there is an API for exporting image definitions from fog?
https://forums.fogproject.org/topic/12026/powershell-api-module
The other option might be to write some mysql code to export the image def table on the root fog server then to import it on the remote fog server end. This could be added to your cron job as part of the image movements.
As long as the receving end fog server doesn’t create its own images the export and import with mysql should be pretty clean. If the receiving end fog server also created images then there is the problem of duplicate image IDs in the database.
Sorry I just saw this
100% you can get image definitions from the api and you could then store them in json files. It would be a lot simpler, easier and safer than direct database calls in my opinion and it handles the whole column sql stuff.
Here’s a quick sample of what you might do
On the source server with the original image install and configure the fogApi powershell module.
Open up a powershell console
#if you're new to powershell you may need this Set-executionpolicy RemoteSigned; #install and import the module Install-Module FogApi Import-Module FogApi; # go obtain your fog server and user api tokens from the fog web gui then put them in this command Set-FogServerSettings -fogApiToken 'your-server-token' -fogUserToken 'your-user-token' fog-server 'your-fog-server-hostname';You’ll need to do that above setup for each location to connect to the api
Now you can get the images and store them as json files, could do 1 big one and could use other file formats, this example will create a json file for each image you have and store it in \server\share\fogImages which you should of course to change to some share you have access to.
This is a function you could paste into powershell and change that path using the parameter-exportPath "yourPath\here"function Export-FogImageDefinitions { [cmdletBinding()] param ( $exportPath = "\\sever\share\fogImages" ) $images = Get-FogImages; $images | Foreach-object { $name = $_.name; $_ | ConvertTo-Json | Out-File -encoding oem "$exportPath\$name.json"; } }So you can copy and paste that (or save it into a .ps1 you dotsource, I may also just add it as a function in the fogAPi module as it would be handy for other users especially when migrating servers.)
You’d run it like this (after having setup your fog api connection
Export-FogImageDefinitions -exportPth "some\path\here"
Now you have them all in json format on some share so you need an import commandNow this one I can’t easily test at the moment and may need a little bit of TLC, I based the fields to pass in on the ones defined in the matching class https://github.com/FOGProject/fogproject/blob/master/packages/web/lib/fog/image.class.php
This is the function you’d run on the other fog servers after configuring the powershell module for the destination fog server on that destination network.
EDIT: I adjusted this one after some testing. The api will ignore the old id automatically so it doesn’t matter if you pass that and you can pass all the other information that was exported as well, so no need to filter out anything with Select-Object, in fact you can just pass the raw json files
Function Import-FogImageDefinitions { [cmdletBinding()] param( $importPath = "/images/imageDefinitions" ) $curImages = Get-FogImages; #get the json files you exported into the given path $imageJsons = Get-ChildItem $importPath\*.json; $imageJsons | Foreach-Object { # get the content of the json, convert it to an object, and create the image definition #create the image on the new server if it doesn't already exist if ($curImages.name -contains $_.baseName) { #this will assume the exported definition is the most up to date definition and update the image definition. Update-FogObject -type object -coreObject image -jsonData (Get-Content $_.Fullname -raw); } else { New-FogObject -type object -coreObject image -jsondata (Get-Content $_.Fullname -raw) } } }So you copy paste this function into powershell and run
import-fogImageDefinitions -importPath \\path\to\where\you\exported\imagesThat should do the trick.
Also, I believe that all of this will work in the linux version of powershell as well if you don’t have windows in your environment or if you wanted to have all of this running on the fog servers themselves. I also didn’t include what hosts have it assigned as that would probably be different on different servers. That’s also possible to export and import if the hosts are all the same.
You could also take this example and expand on it and get things automated via scheduled tasks on a windows system or cron on the fog servers so it essentially auto-replicates these definitions as you add new ones. If you want more information or more guidance on using the api for this let me know
-
RE: Surface Go 1 can't access fog host variables in FOS during postdownload scriptsposted in Bug Reports
@Sebastian-Roth The variables you don’t recognize are part of post installation scripts, I haven’t modified any php classes.
I will see if I can get that output on monday, we’ve now deployed all of our surface go 1’s back to their users but I can probably nab one for a few minutes if I get in early enough.
I can also try a different ipxe boot file for good measure. I use ipxe.efi maybe snponly.efi will load things differently and yield different results
-
RE: Surface Go 1 can't access fog host variables in FOS during postdownload scriptsposted in Bug Reports
TL;DR
Some variables behaving weirdly in postdownload scripts on certain hardware.
-
Surface Go 1 can't access fog host variables in FOS during postdownload scriptsposted in Bug Reports
So we’re using a postdownload script to inject ad join information into an unattend file.
This works great except on first generation microsoft surface go’sFor some reason they are missing the host specific variables during imaging
i.e., if I start a debug imaging task on a VM and run
$then tab to view all defined variables I see something like this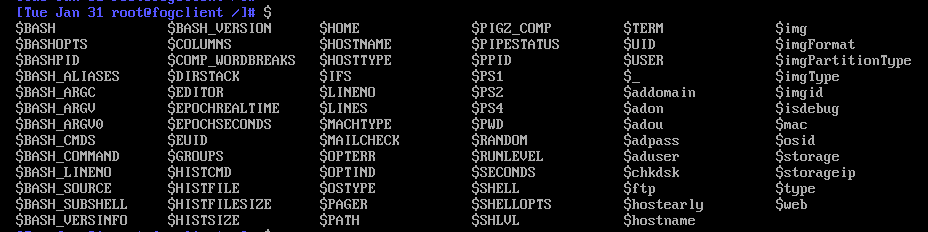
In a debug session on a surface go 1, I get only the build-int all caps system variables.
If in the same debug session I manually load the funcs.sh
source /usr/share/fog/lib/funcs.sh [Tue Jan 31 root@fogclient /images/postdownloadscripts]# $ $BASH $EUID $PAGER $UID $isdebug $BASHOPTS $GROUPS $PATH $USER $ismajordebug $BASHPID $HISTCMD $PIGZ_COMP $_ $loglevel $BASH_ALIASES $HISTFILE $PIPESTATUS $addomain $mac $BASH_ARGC $HISTFILESIZE $PPID $adon $netbiosdomain $BASH_ARGV $HISTSIZE $PS1 $adou $osid $BASH_ARGV0 $HOME $PS2 $adpass $ramdisk_size $BASH_CMDS $HOSTNAME $PS4 $aduser $root $BASH_COMMAND $HOSTTYPE $PWD $chkdsk $rootfstype $BASH_LINENO $IFS $RANDOM $consoleblank $storage $BASH_SOURCE $LINENO $REG_LOCAL_MACHINE_7 $domainJoinStr $storageip $BASH_SUBSHELL $LINES $REG_LOCAL_MACHINE_XP $ftp $type $BASH_VERSINFO $LOGNAME $SECONDS $hostearly $unattend $BASH_VERSION $MACHTYPE $SHELL $hostname $unattends $COLUMNS $MAIL $SHELLOPTS $img $var $COMP_WORDBREAKS $MAILCHECK $SHLVL $imgFormat $web $DIRSTACK $OLDPWD $SSH_CLIENT $imgPartitionType $EDITOR $OPTERR $SSH_CONNECTION $imgType $EPOCHREALTIME $OPTIND $SSH_TTY $imgid $EPOCHSECONDS $OSTYPE $TERM $initrdI can then see the variables however,
$addomainis null when it should not be. The other ad related variables are populated.
But then if I manually setaddomain='mydomain.com'or try putting that into my postdownload script, it still gets lost while running the postdownload script, which only occurs on this hardware.If I load the funcs.sh, set the addomain variable manually, and then paste in just the sed commands I have for updating the unattend file, it works as it should. But this requires a debug session and a lot of manual effort.
so if I run
. /usr/share/fog/lib/funcs.sh #I typically do this in a loop of all standard unattend paths. like this #unattends=("/ntfs/Unattend.xml" "/ntfs/Windows/System32/Sysprep/Unattend.xml" "/ntfs/Windows/Panther/unattend.xml" "/ntfs/Windows/Panther/Unattend.xml") #but for testing purposes, (and since pasting longer snippets into a ssh bash shell can be finicky) just doing one path unattend="/ntfs/Windows/System32/Sysprep/Unattend.xml" cp $unattend $unattend.old domainJoinStr="<JoinDomain></JoinDomain>\n\t\t<MachineObjectOU></MachineObjectOU>\n\t\t<Credentials>\n\t\t\t<Domain></Domain>\n\t\t\t<Password></Password>\n\t\t\t<Username></Username>\n\t\t</Credentials>" echo -en "\n\nInjecting Unattend Join fields into unattend for Dynamic update....\n" echo -en "\n\nInjecting Unattend Join fields into unattend for Dynamic update....\n" >> $updateUnattendLog # get the value of the workgroup to set as the netbios domain for the domain login netbiosdomain=`sed -n '/JoinWorkgroup/{s/.*<JoinWorkgroup>//;s/<\/JoinWorkgroup.*//;p;}' $unattend` #replace the workgroup join string with the domain tags to be updated sed -i -e "s|<JoinWorkgroup>${netbiosdomain}</JoinWorkgroup>|${domainJoinStr}|g" $unattend >/dev/null 2>&1 echo -en "\n\nSetting Dynamic Unattend fields - \n\nDeviceForm: ${DeviceForm}\nComputer Name: ${hostname}\nJoining Domain: ${addomain}\nWill be in OU: ${adou}\n" echo -en "\n\nSetting Dynamic Unattend fields - \n\nDeviceForm: ${DeviceForm}\nComputer Name: ${hostname}\nJoining Domain: ${addomain}\nWill be in OU: ${adou}\n" >> $updateUnattendLog sed -i \ -e "s|<DeviceForm>3</DeviceForm>|<DeviceForm>${DeviceForm}</DeviceForm>|g" \ -e "s|<ComputerName></ComputerName>|<ComputerName>${hostname}</ComputerName>|g" \ -e "s|<Name>\*</Name>|<Name>${hostname}</Name>|g" \ -e "s|<Password></Password>|<Password>${adpass}</Password>|g" \ -e "s|<Username></Username>|<Username>${aduser}</Username>|g" \ -e "s|<Domain></Domain>|<Domain>${netbiosdomain}</Domain>|g" \ -e "s|<MachineObjectOU></MachineObjectOU>|<MachineObjectOU>${adou}</MachineObjectOU>|g" \ -e "s|<JoinDomain></JoinDomain>|<JoinDomain>${addomain}</JoinDomain>|g" $unattend >/dev/null 2>&1 echo -en "\n\nRemoving Workgroup join section and backup unattend as adding domain join was a success...\n" echo -en "\n\nRemoving Workgroup join section and backup unattend as adding domain join was a success...\n" >> $updateUnattendLog rm -f $unattend.old sed -i "/<JoinWorkgroup>/d" $unattend >/dev/null 2>&1 sed -i "/<MachinePassword>/d" $unattend >/dev/null 2>&1This works, but running the same from a postdownload script loses the funcs.sh functions and some of the ad related variables. Luckily the aduser and adpass variables work so I can hardcode in a failsafe of my domain and a default ou, but putting a machine in the wrong ou then requires additional failsafes to be sure it gets the correct policies, which I do also have for my provisioning process, but things run much smoother when it joins the correct ou from the get go.
Any thoughts on this weird one?
Also, here is how the script is called within postdownload scripts.
fog.postdownload is called
#!/bin/sh ## This file serves as a starting point to call your custom postimaging scripts. ## <SCRIPTNAME> should be changed to the script you're planning to use. ## Syntax of post download scripts are #. ${postdownpath}<SCRIPTNAME> bash ${postdownpath}fog.custominstallfog.custominstall calls my driver injector script (which is working fine for this) and then my unattend editor
#!/bin/bash . /usr/share/fog/lib/funcs.sh [[ -z $postdownpath ]] && postdownpath="/images/postdownloadscripts/" echo $osid case $osid in 5|6|7|9) clear [[ ! -d /ntfs ]] && mkdir -p /ntfs getHardDisk if [[ -z $hd ]]; then handleError "Could not find hdd to use" fi getPartitions $hd for part in $parts; do umount /ntfs >/dev/null 2>&1 fsTypeSetting "$part" case $fstype in ntfs) dots "Testing partition $part" ntfs-3g -o force,rw $part /ntfs ntfsstatus="$?" if [[ ! $ntfsstatus -eq 0 ]]; then echo "Skipped" continue fi if [[ ! -d /ntfs/windows && ! -d /ntfs/Windows && ! -d /ntfs/WINDOWS ]]; then echo "Not found" umount /ntfs >/dev/null 2>&1 continue fi echo "Success" break ;; *) echo " * Partition $part not NTFS filesystem" ;; esac done if [[ ! $ntfsstatus -eq 0 ]]; then echo "Failed" debugPause handleError "Failed to mount $part ($0)\n Args: $*" fi echo "Done" debugPause . ${postdownpath}fog.copydrivers . ${postdownpath}fog.updateunattend debugPause umount /ntfs ;; *) echo "Non-Windows Deployment" debugPause return ;; esacThen this is the contents of fog.updateunattend with edits for information sensitivity
#!/bin/bash # Value Device form Description # 0 Unknown Use this value if your device does not fit into any of the other device form factors. # 1 Phone A typical smartphone combines cellular connectivity, a touch screen, rechargeable power source, and other components into a single chassis. # 2 Tablet A device with an integrated screen that's less than 18". It combines a touch screen, rechargeable power source, and other components into a single chassis with an optional attachable keyboard. # 3 Desktop A desktop PC form factor traditional comes in an upright tower or small desktop chassis and does not have an integrated screen. # 4 Notebook A notebook is a portable clamshell device with an attached keyboard that cannot be removed. # 5 Convertible A convertible device is an evolution of the traditional notebook where the keyboard can be swiveled, rotated or flipped, but not completely removed. It is a blend between a traditional notebook and tablet, also called a 2-in-1. # 6 Detachable A detachable device is an evolution of the traditional notebook where the keyboard can be completely removed. It is a blend between a traditional notebook and tablet, also called a 2-in-1. # 7 All-in-One An All-in-One device is an evolution of the traditional desktop with an attached display. # 8 Stick PC A device that turns your TV into a Windows computer. Plug the stick into the HDMI slot on the TV and connect a USB or Bluetooth keyboard or mouse. # 9 Puck A small-size PC that users can use to plug in a monitor and keyboard. # A Surface Hub Microsoft Surface Hub # B Head-mounted display A holographic computer that is completely untethered - no wires, phones, or connection to a PC needed. # C Industry handheld A device screen less than 7” diagonal designed for industrial solutions. May or may not have a cellular stack. # D Industry tablet A device with an integrated screen greater than 7” diagonal and no attached keyboard designed for industrial solutions as opposed to consumer personal computer. May or may not have a cellular stack. # E Banking A machine at a bank branch or another location that enables customers to perform basic banking activities including withdrawing money and checking one's bank balance. # F Building automation A controller for industrial environments that can include the scheduling and automatic operation of certain systems such as conferencing, heating and air conditioning, and lighting. # 10 Digital signage A computer or playback device that's connected to a large digital screen and displays video or multimedia content for informational or advertising purposes. # 11 Gaming A device that's used for playing a game. It can be mechanical, electronic, or electromechanical equipment. # 12 Home automation A controller that can include the scheduling and automatic operation of certain systems including heating and air conditioning, security, and lighting. # 13 Industrial automation Computers that are used to automate manufacturing systems such as controlling an assembly line where each station is occupied by industrial robots. # 14 Kiosk An unattended structure that can include a keyboard and touch screen and provides a user interface to display interactive information and allow users to get more information. # 15 Maker board A low-cost and compact development board that's used for prototyping any number IoT-related things. # 16 Medical Devices built specifically to provide medical staff with information about the health and well-being of a patient. # 17 Networking A device or software that determines where messages, packets, and other signals will go next. # 18 Point of Service An electronic cash register or self-service checkout. # 19 Printing A printer, copy machine, or a combination of both. # 1A Thin client A device that connects to a server to perform computing tasks as opposed to running apps locally. # 1B Toy A device used solely for enjoyment or entertainment. # 1C Vending A machine that dispenses items in exchange for payment in the form of coin, currency, or credit/debit card. # 1D Industry other A device that doesn't fit into any of the previous categories. . /usr/share/fog/lib/funcs.sh ceol=`tput el`; make=`dmidecode -s system-manufacturer`; make="${make%.*}"; updateUnattendLog="/ntfs/logs/updateUnattend.log" touch $updateUnattendLog >/dev/null 2>&1 echo -en "\n\n Start of unattend injection log \n\n" > $updateUnattendLog; if [[ "${make}" == "Hewlett-Packard" ]]; then make="hp"; fi if [[ "${make}" == "HP" ]]; then make="hp"; fi if [[ "${make}" == "Hp" ]]; then make="hp"; fi if [[ "${make}" == "VMware, Inc" ]]; then make="VMware"; fi dots "Identifying hardware model, make is ${make}" case $make in [Ll][Ee][Nn][Oo][Vv][Oo]) model=$(dmidecode -s system-version) ;; *[Ii][Nn][Tt][Ee][Ll]* | *[Aa][Ss][Uu][Ss]*) # For the Intel NUC and intel mobo pick up the system type from the # baseboard product name model=$(dmidecode -s baseboard-product-name) ;; *) # Technically, we can remove the Dell entry above as it is the same as this [default] model=$(dmidecode -s system-product-name) ;; esac if [[ -z $model ]]; then # if the model isn't identified then just stick with desktop echo -en "\n\nUnable to identify the hardware for manufacturer ${make} assuming desktop form\n\n"; echo -en "\n\nUnable to identify the hardware for manufacturer ${make} assuming desktop form\n\n" >> $updateUnattendLog; DeviceForm=3; else if [[ "${model}" == "Surface Go" ]]; then echo -en "\n\nSurface Go will also match other generations of Surface Go, adding a 1\n\n" echo -en "\n\nSurface Go will also match other generations of Surface Go, adding a 1\n\n" >> $updateUnattendLog; model="Surface Go 1"; fi echo -en "\n\n${model} Identified, determining device form\n\n"; case $model in *[Aa][Ii][Oo]* | *[Ee]lite[Oo]ne* ) echo -en "\n\n${model} matches a known all-in-one form string, setting device form to all in one\n\n"; echo -en "\n\n${model} matches a known all-in-one form string, setting device form to all in one\n\n" >> $updateUnattendLog; DeviceForm=7 ;; *Surface* | *Switch* | *SA5-271* | *SW512* | *SW312* ) echo -en "\n\n${model} matches a known detachable form string, setting device form to detachble\n\n"; echo -en "\n\n${model} matches a known detachable form string, setting device form to detachble\n\n" >> $updateUnattendLog; DeviceForm=6 ;; *Convertible* | *Yoga* ) echo -en "\n\n${model} matches a known convertible form string, setting device form to convertible\n\n"; echo -en "\n\n${model} matches a known convertible form string, setting device form to convertible\n\n" >> $updateUnattendLog; DeviceForm=5 ;; *ProBook* | *Zbook* | *ThinkPad* | *ThinkBook* | *Sattelite* | *IdeaPad* ) echo -en "\n\n${model} matches a known notebook form string, setting device form to notebook\n\n"; echo -en "\n\n${model} matches a known notebook form string, setting device form to notebook\n\n" >> $updateUnattendLog DeviceForm=4 ;; *[Pp]ro[Dd]esk* | *[Ee]lite[Dd]esk* | *DM* | *Mini* | *Desktop* | *VMware* | *Twr* | *Tower* | *CMT* | *USDT* | *MT* | *ProArt* | *SFF*) echo -en "\n\n${model} matches a known desktop form string, setting device form to desktop\n\n"; echo -en "\n\n${model} matches a known desktop form string, setting device form to desktop\n\n" >> $updateUnattendLog DeviceForm=3 ;; * ) echo -en "\n\n${model} doesn't match any known deviceForm strings, assuming desktop device form\n\n"; echo -en "\n\n${model} doesn't match any known deviceForm strings, assuming desktop device form\n\n" >> $updateUnattendLog DeviceForm=3 ;; esac echo -en "\n\nDevice form code is ${DeviceForm}\n\n" echo -en "\n\nDevice form code is ${DeviceForm}\n\n" >> $updateUnattendLog fi unattends=("/ntfs/Unattend.xml" "/ntfs/Windows/System32/Sysprep/Unattend.xml" "/ntfs/Windows/Panther/unattend.xml" "/ntfs/Windows/Panther/Unattend.xml") for unattend in ${unattends[@]}; do [[ ! -f $unattend ]] && break . /usr/share/fog/lib/funcs.sh dots "Preparing Sysprep File at $unattend" #update unattend files if an Unattend.xml file is present if [[ -f "/images/drivers/Unattend.xml" ]]; then echo -en "\n\nUnattend.xml patch file detected, updating the Unattend.xml file baseline\n\n"; echo -en "\n\nUnattend.xml patch file detected, updating the Unattend.xml file baseline\n\n" >> $updateUnattendLog rsync -aqzz "/images/drivers/Unattend.xml" $unattend; else echo -en "\n\nNo Unattend.xml patch file detected, skipping update of unattend.xml file baseline and just updating contents\n\n"; echo -en "\n\nNo Unattend.xml patch file detected, skipping update of unattend.xml file baseline and just updating contents\n\n" >> $updateUnattendLog fi #echo "File update Done" debugPause # [[ -z $addomain ]] && continue #if there is a domain to join, then join it in the unattend, otherwise just set computername if [[ $adon=="1" ]]; then dots "Set PC to join the domain with correct name and OU" if [[ -z $addomain ]]; then #set the default domain to join if missing addomain='mydomain.com' fi if [[ -z $adou ]]; then #set the default ou if missing adou='OU=default,DC=mydomain,DC=com' fi #make a backup of the unattend before editing cp $unattend $unattend.old domainJoinStr="<JoinDomain></JoinDomain>\n\t\t<MachineObjectOU></MachineObjectOU>\n\t\t<Credentials>\n\t\t\t<Domain></Domain>\n\t\t\t<Password></Password>\n\t\t\t<Username></Username>\n\t\t</Credentials>" echo -en "\n\nInjecting Unattend Join fields into unattend for Dynamic update....\n" echo -en "\n\nInjecting Unattend Join fields into unattend for Dynamic update....\n" >> $updateUnattendLog # get the value of the workgroup to set as the netbios domain for the domain login netbiosdomain=`sed -n '/JoinWorkgroup/{s/.*<JoinWorkgroup>//;s/<\/JoinWorkgroup.*//;p;}' $unattend` #replace the workgroup join string with the domain tags to be updated sed -i -e "s|<JoinWorkgroup>${netbiosdomain}</JoinWorkgroup>|${domainJoinStr}|g" $unattend >/dev/null 2>&1 echo -en "\n\nSetting Dynamic Unattend fields - \n\nDeviceForm: ${DeviceForm}\nComputer Name: ${hostname}\nJoining Domain: ${addomain}\nWill be in OU: ${adou}\n" echo -en "\n\nSetting Dynamic Unattend fields - \n\nDeviceForm: ${DeviceForm}\nComputer Name: ${hostname}\nJoining Domain: ${addomain}\nWill be in OU: ${adou}\n" >> $updateUnattendLog sed -i \ -e "s|<DeviceForm>3</DeviceForm>|<DeviceForm>${DeviceForm}</DeviceForm>|g" \ -e "s|<ComputerName></ComputerName>|<ComputerName>${hostname}</ComputerName>|g" \ -e "s|<Name>\*</Name>|<Name>${hostname}</Name>|g" \ -e "s|<Password></Password>|<Password>${adpass}</Password>|g" \ -e "s|<Username></Username>|<Username>${aduser}</Username>|g" \ -e "s|<Domain></Domain>|<Domain>${netbiosdomain}</Domain>|g" \ -e "s|<MachineObjectOU></MachineObjectOU>|<MachineObjectOU>${adou}</MachineObjectOU>|g" \ -e "s|<JoinDomain></JoinDomain>|<JoinDomain>${addomain}</JoinDomain>|g" $unattend >/dev/null 2>&1 if [[ ! $? -eq 0 ]]; then echo -en "\n\nFailed to update user, pass, ou, and domain setter, set just computername and deviceform instead and using simplified unattend file\n" echo -en "\n\nFailed to update user, pass, ou, and domain setter, set just computername and deviceform instead and using simplified unattend file\n" >> $updateUnattendLog echo -en "\n\Restoring unattend file from before domain join attempt\n" echo -en "\n\Restoring unattend file from before domain join attempt\n" >> $updateUnattendLog mv $unattend.old $unattend -f echo -en "\n\nSetting Dynamic Unattend fields - \n\nDeviceForm: ${DeviceForm}\nComputer Name: ${hostname}" echo -en "\n\nSetting Dynamic Unattend fields - \n\nDeviceForm: ${DeviceForm}\nComputer Name: ${hostname}" >> $updateUnattendLog #rsync -aqzz "/images/drivers/workgroup-unattend.xml" $unattend; debugPause sed -i \ -e "s|<DeviceForm>3</DeviceForm>|<DeviceForm>${DeviceForm}</DeviceForm>|g" \ -e "s|<ComputerName></ComputerName>|<ComputerName>${hostname}</ComputerName>|g" \ -e "s|<Name>\*</Name>|<Name>${hostname}</Name>|g" $unattend >/dev/null 2>&1 if [[ ! $? -eq 0 ]]; then echo -en "\nFailed again after using failsafe unattend\n" echo -en "\nFailed again after using failsafe unattend\n" >> $updateUnattendLog debugPause handleError "Failed to update user, pass, ou, and domain setter and then failed the failsafe with no domain" fi else echo -en "\n\nRemoving Workgroup join section and backup unattend as adding domain join was a success...\n" echo -en "\n\nRemoving Workgroup join section and backup unattend as adding domain join was a success...\n" >> $updateUnattendLog rm -f $unattend.old sed -i "/<JoinWorkgroup>/d" $unattend >/dev/null 2>&1 sed -i "/<MachinePassword>/d" $unattend >/dev/null 2>&1 if [[ ! $? -eq 0 ]]; then echo "Failed" debugPause handleError "Failed to remove the Workgroup setter" fi fi echo -en "\n\nDone updating $unattend\n" echo -en "\n\nDone updating $unattend\n" >> $updateUnattendLog debugPause else echo -en "\n\nNo domain to join variable present, just setting deviceform and computer name and using simplified unattend file\n" echo -en "\n\nNo domain to join variable present, just setting deviceform and computer name and using simplified unattend file\n" >> $updateUnattendLog echo -en "\n\nSetting Dynamic Unattend fields - \n\nDeviceForm: ${DeviceForm}\nComputer Name: ${hostname}" echo -en "\n\nSetting Dynamic Unattend fields - \n\nDeviceForm: ${DeviceForm}\nComputer Name: ${hostname}" >> $updateUnattendLog # rsync -aqzz "/images/drivers/workgroup-unattend.xml" $unattend; debugPause sed -i \ -e "s|<DeviceForm>3</DeviceForm>|<DeviceForm>${DeviceForm}</DeviceForm>|g" \ -e "s|<ComputerName></ComputerName>|<ComputerName>${hostname}</ComputerName>|g" \ -e "s|<Name>\*</Name>|<Name>${hostname}</Name>|g" $unattend >/dev/null 2>&1 if [[ ! $? -eq 0 ]]; then echo "Failed" debugPause handleError "Failed to set workgroup join fields" fi fi done -
RE: API PUT request not workingposted in FOG Problems
@brian-mainake Have you tried the powershell module for the api?
It looks like you’re trying to add a primary mac, I have this function https://fogapi.readthedocs.io/en/latest/commands/Add-FogHostMac/ that can do that.
You can look at the code at this link https://github.com/darksidemilk/FogApi/blob/master/FogApi/Public/Add-FogHostMac.ps1 and it will give you an idea of how I’m getting that working. As with any api they syntax can be tricky at times but it’s pretty intuitive once you get a couple calls working. -
RE: Powershell API Moduleposted in Tutorials
@jj-fullmer
A new Major version has been released along with a quick feature revision shortly aftersee
https://github.com/darksidemilk/FogApi/releases/tag/2208.3.0
and
https://github.com/darksidemilk/FogApi/releases/tag/2208.3.1for details on what’s been added.
Some highlights include
Deploy-FogImage and Capture-FogImage functions to start deploy and capture tasks on fog hosts from powershell both instant and scheduled.
You could always do this, but it’s now simplified in helper functions. -
RE: Powershell API Moduleposted in Tutorials
@chris-whiteley Sorry for the insanely delayed reply.
So you’re looking to find a host by the serial number? And then get the last time it was imaged?
I was coming here to post information on my recent update, but this sounded useful so I went ahead and implemented getting a foghost by the serialnumber in the inventory field and even aget-lastimagetimefunction that will default to prompting you to scan a serial number barcode
These will be published shortly.-JJ
-
RE: FOG API add snapin, run task and then deleteposted in FOG Problems
@Chris-Whiteley I finally had some time to work on the module and created a
Start-FogSnapinfunction that can deploy a single snapin task.See also https://fogapi.readthedocs.io/en/latest/commands/Start-FogSnapin/
-
RE: Image capture PXE boot hangs after tftpposted in FOG Problems
@geekyjm Is secure boot disabled on the VM? Have you tried setting a different boot file, i.e. ipxe.efi instead of snponly.efi?
-
RE: PXE Boot not working - Windows 2019 DHCPposted in Windows Problems
@multipass Is this a completely new setup or was it working and it broke?
The BIOS and UEFI co-existence page might need some updating, but I believe it’s still accurate from the last time I utilized it. I don’t use the co-existence anymore because we were able to get all uefi machines.I’d try to get it work without the vendor policies first and then add those after.
If you have a way to mount the TFTP share of fog elsewhere, that would be a good test to make sure that’s running correctly
I also find setting the options for DHCP per scope is helpful -
RE: Snapin Update in Snapin Management Edit changes snapin File Name to "1"posted in Bug Reports
- Go to a snapin in the GUI
- upload a new file for the snapin, or a new version of the same file
- look at /opt/fog/snapins and see a file named
1instead of your updated file.